The Tomb of Queen Nefertari, located in Egypt’s Valley of the Queens, is one of the most extraordinary monuments of ancient Egyptian civilization. Dating back to around 1255 BCE, this tomb was built for Queen Nefertari, the cherished wife of Pharaoh Ramses II, during the height of the New Kingdom. Her final resting place showcases breathtaking artistry and offers deep insights into Egyptian beliefs about the afterlife.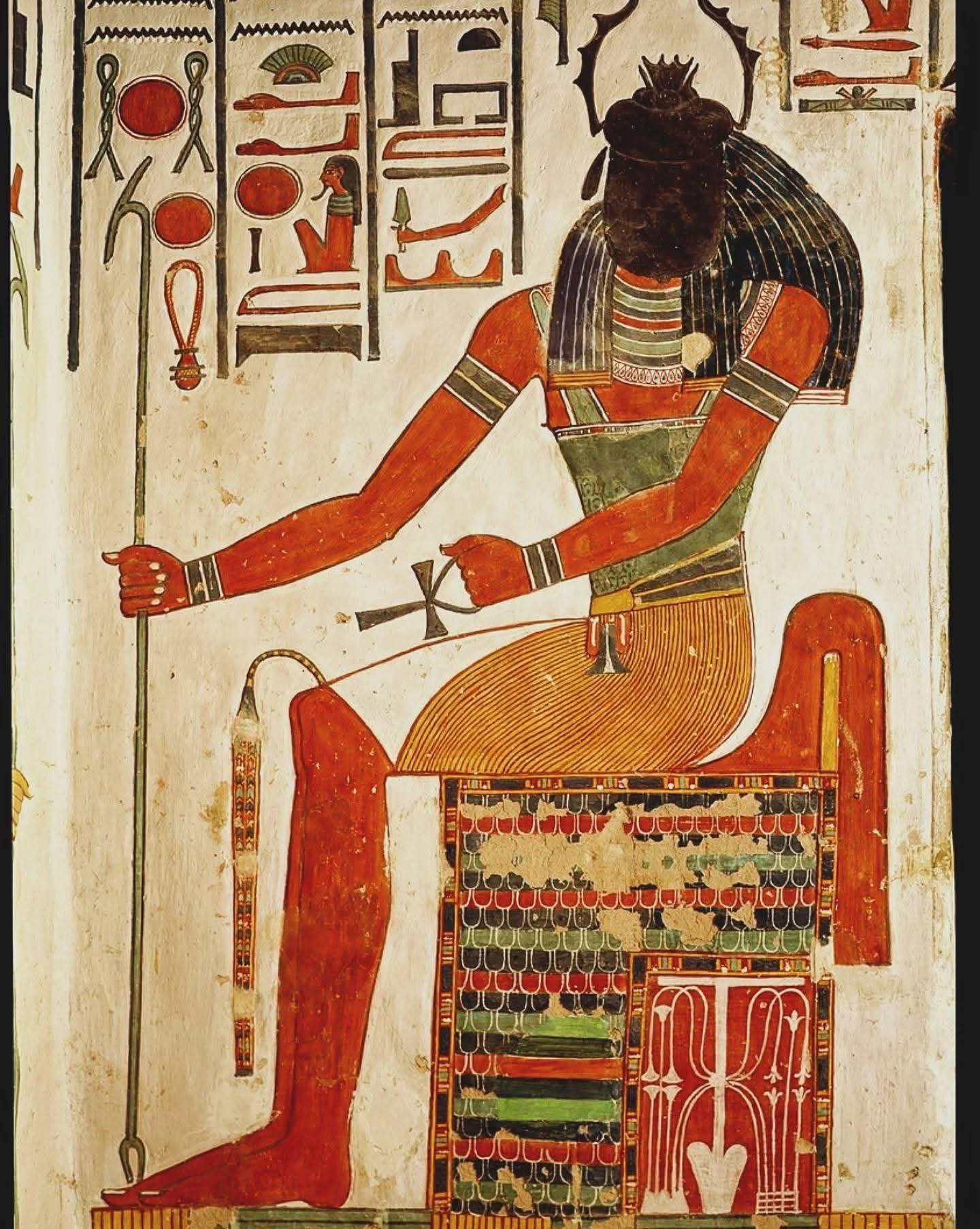
Historical Significance of Queen Nefertari’s Tomb
A Queen of Great Influence
Queen Nefertari was not just the principal wife of Ramses II but also one of the most powerful and educated women of her time. Her role in diplomatic and religious affairs elevated her status in ancient Egyptian society.
The Valley of the Queens as a Sacred Burial Ground
The Valley of the Queens served as a necropolis for royal women and children. Located on the west bank of Luxor, it was chosen for its spiritual significance and proximity to the Valley of the Kings.
Construction During the New Kingdom
The tomb was constructed during the 19th Dynasty, reflecting the architectural and artistic advancements of the New Kingdom period. Its elaborate design and intricate paintings set it apart from other tombs in the valley.
Artistic Features of the Tomb of Queen Nefertari
Stunning Wall Paintings and Colors
The tomb is renowned for its vivid wall paintings, which remain remarkably well-preserved. Bright pigments and lifelike imagery depict scenes of Nefertari in the presence of gods, navigating the journey to the afterlife.
Depictions of the Afterlife
One of the most iconic images shows Queen Nefertari receiving blessings from Osiris, the god of the underworld. These depictions represent the ancient Egyptian belief in eternal life and the soul’s journey through the underworld.
Symbolism in Hieroglyphs and Art
Every symbol, color, and hieroglyph in the tomb was deliberately chosen to convey messages of protection, divine favor, and safe passage into the afterlife. The artistry blends religious meaning with exceptional craftsmanship.
Cultural and Spiritual Importance
Reflection of Ancient Egyptian Beliefs
The tomb is a powerful representation of the ancient Egyptians’ belief in Ma’at—order, harmony, and cosmic balance. Nefertari’s journey to the afterlife is portrayed with reverence and precision.
A Testament to Love and Legacy
The grandeur of the tomb also reflects Ramses II’s deep love and admiration for Nefertari. He ensured her burial place would be a masterpiece, fit for a queen of her stature.
Preservation and Modern Discoveries
Discovered in 1904, the tomb has since undergone restoration to protect its delicate artwork. It remains one of the most visited and studied sites in Luxor, drawing scholars, tourists, and art lovers from around the world.

CÁC TIN KHÁC
Mary Walton: The Forgotten Inventor Who Helped Clean Up America’s Cities
Tomb of Queen Nefertari in the Valley of the Queens, Egypt
Discover the Hypostyle Hall of the Temple of Hathor at Dendera
Venus de Losange: Unveiling the Mystery of a 20,000-Year-Old Paleolithic Icon