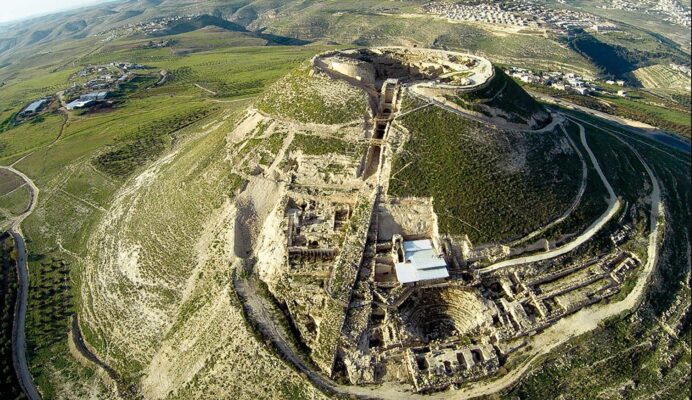
Herodium, King Herod’s Palace, is a remarkable archaeological site in the Judean Desert, near Bethlehem, Israel. Built between 23-15 BC, it served as a multifaceted complex, functioning as a fortress, palace, and the final resting place of Herod the Great.
The Architectural Marvel of Herodium
Herodium’s architectural design and construction reflect Herod the Great’s ambition and engineering prowess.
Multifunctional Complex
Herodium was designed to serve multiple purposes, combining the functions of a fortress, palace, and burial site.

- Fortress Function:
- The site’s strategic location and fortified design served as a defensive stronghold, ensuring Herod’s security.
- Its elevated position provided a commanding view of the surrounding landscape.
- Palace Residence:
- Herodium featured luxurious living quarters, showcasing Herod’s wealth and status.
- The palace was designed for comfort and grandeur, reflecting Herod’s royal lifestyle.
- Burial Site:
- Herodium was chosen as Herod’s final resting place, adding a significant religious and historical dimension to the site.
- The unique circular structure is believed to be his tomb.
Luxurious Amenities
The palace complex included various amenities, highlighting the opulence of Herod’s court.

- Opulent Living Quarters:
- The palace featured lavishly decorated living quarters, reflecting Herod’s royal lifestyle.
- These quarters were designed for comfort and grandeur, showcasing his wealth.
- Bathhouses:
- The presence of bathhouses indicates the importance of hygiene and leisure in Herod’s court.
- These facilities were a common feature in Roman-influenced architecture.
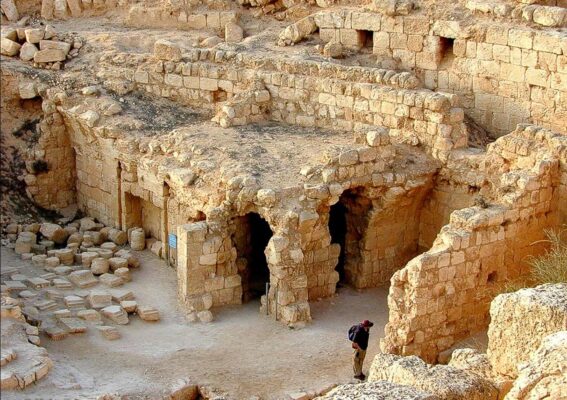
- Circular Tomb Structure:
- The distinctive circular structure, believed to be Herod’s tomb, is a unique architectural feature.
- Its design and construction reflect the importance of the burial site.
Engineering Prowess
The construction of Herodium demonstrates Herod’s advanced engineering skills and architectural vision.

- Strategic Location:
- The site’s strategic location in the Judean Desert highlights Herod’s understanding of defensive architecture.
- Its elevated position provided a natural advantage.
- Construction Techniques:
- The use of advanced construction techniques, including the creation of artificial hills, showcases Herod’s engineering prowess.
- These techniques allowed for the creation of a monumental structure.
- Architectural Vision:
- Herodium’s design reflects Herod’s grand architectural vision, combining functionality with aesthetic appeal.
- The site stands as a testament to his ambition and skill.
Herodium’s Historical and Archaeological Significance
Herodium’s historical and archaeological significance lies in its connection to King Herod the Great and its contribution to our understanding of ancient Judean history.
Herod the Great’s Legacy
Herodium is a significant historical landmark, providing insights into the life and reign of King Herod the Great.

- Connection to Herod:
- The site’s direct connection to Herod the Great makes it a crucial historical landmark.
- It offers a tangible link to his reign and legacy.
- Architectural Vision:
- Herodium showcases Herod’s architectural vision and his ability to create monumental structures.
- The site reflects his ambition and engineering skills.
- Historical Context:
- The site provides valuable historical context for understanding the political and cultural landscape of ancient Judea.
- It sheds light on the Roman influence in the region.
Archaeological Discoveries
Archaeological discoveries at Herodium have provided valuable insights into the site’s history and function.
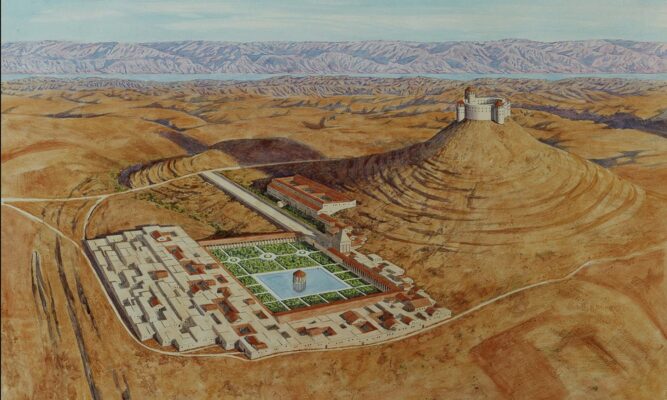
- Palace Remains:
- The impressive remains of the palace complex offer insights into the daily life and culture of Herod’s court.
- These remains provide a glimpse into the opulence of the era.
- Tomb Discovery:
- The discovery of Herod’s tomb has added a significant historical and archaeological dimension to the site.
- It confirms the site’s role as his final resting place.
- Artifacts and Findings:
- Artifacts and findings from the site contribute to our understanding of ancient Judean history and culture.
- These discoveries provide valuable information about the site’s inhabitants and their practices.
Landmark Status
Herodium’s status as a significant historical and archaeological landmark attracts researchers and visitors from around the world.
- Tourist Attraction:
- The site’s historical significance and architectural beauty make it a popular tourist attraction.
- It draws visitors interested in ancient history and archaeology.
- Research Site:
- Herodium serves as an important research site for archaeologists and historians studying ancient Judea.
- Ongoing excavations and studies contribute to our understanding of the site.
- Cultural Heritage:
- The site’s preservation and study contribute to the preservation of cultural heritage in the region.
- It ensures that the stories and lessons of the past are not forgotten.
Herodium stands as a testament to King Herod the Great’s grand architectural vision and remains a significant historical and archaeological landmark in the Judean Desert. Its multifaceted design and rich history continue to captivate and educate visitors and researchers alike.

CÁC TIN KHÁC
Mary Walton: The Forgotten Inventor Who Helped Clean Up America’s Cities
Tomb of Queen Nefertari in the Valley of the Queens, Egypt
Discover the Hypostyle Hall of the Temple of Hathor at Dendera
Venus de Losange: Unveiling the Mystery of a 20,000-Year-Old Paleolithic Icon